Recycling flexible PU Foam Residues
Recycling flexible PU Foam Residues
Technology:
H&S technology of flexible PU foam recycling is based on optimized acidolysis method where PU residues are being dissolved in a mixture of carboxylic acids and basic polyol. In comparison to previous conversion methods, polyols generated by H&S technology have good reactivity and do not contain primary aromatic amines (methylene and toluene diamine) which are hazardous and not acceptable in bedding and upholstery foams.
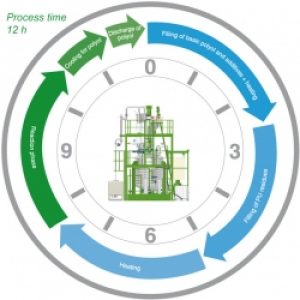
Process sequence and duration:
Raw materials required for the process:
Flexible PU foam residues:
Clean shredded residues from slabstock production (industrial waste):
– The residues must be free from contaminations of other polymers, paper or metals.
– The residues shoul be separated in case of essential chemical differences, for example MDI and TDI foam, conventional and HR foams, etc.
Basic polyether polyol for flexible foam:
Molar mass: 2.000 – 6.000 g / mol
Viscosity: 600 – 3.000 mPas
Hydroxyl number: 36 à 56 mg de KOH / g
Water content: <0,2%
Carboxylic acids:
2 dicarboxylic acids
Catalyst
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————–
Example recipe:
Raw Materials %
PU foam industrial waste 42
Acids 12
Catalyst 2
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————–
Properties of the recovered polyol:
Hydroxyl number: 48 ± 4 mg KOH/g
Acid number: < 1,1 mg KOH/g
Amine number: < 7 mg KOH/g
Viscosity: 4.000 – 7.500 mPas
Appearance: viscous liquid of light brown to dark brown color – depending on the color of the foam residues
No primary aromatic amines (no TDA or MDA)!
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————–
Recovered polyol can substitute:
up to 20% of conventional polyol for production of bedding and furniture PU foam
higher percentage for technical foams

———————————————————————————————————————————————————————–
without any influence on the physical and mechanical properties of the PU foam.
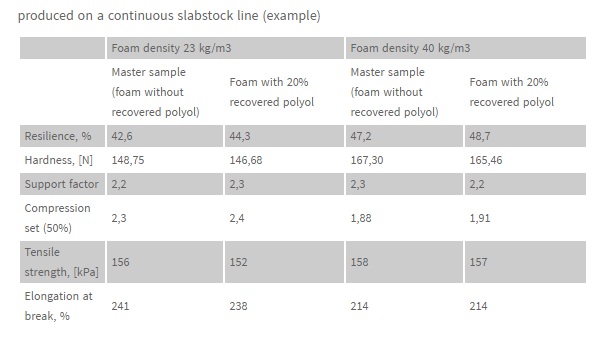
All parameters line compression set, hardness, resilience, support factor, tensile strength and elongation at break are in the range of the control samples.
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————–
The costs to manufacture recoverd polyol are 25-30% percent lower than the market price of the original basic polyether polyol.
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————–
Properties of the conventional PU foam produced with 20% recovered polyol:
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————–
Repeatable recycling of the flexible PU foam:
The process based on H&S technology enables to convert slabstock foam residues into polyol for at least 20 cycles without considerable influence on the chemical and mechanical properties of the recycled polyol and resulted PU foam.
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————–
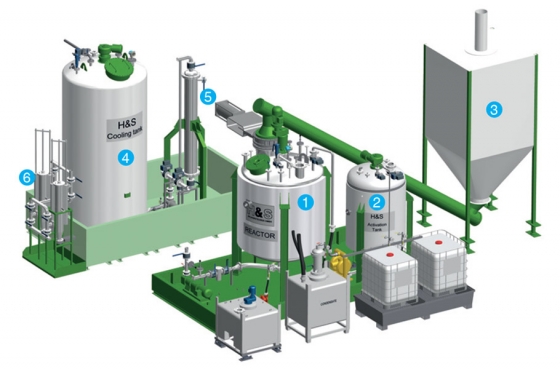
Reactor and peripheral equipment:
core unit
1. Réactor
2. Activation tank
3. Feeding system for PU residues
4. Cooling tank
5. Heat exchanger
6. Filtration system
Flexible foam reactors can be supplied with batch capacity from 1t to 5t.